In-field hyperspectral imaging: An overview on the ground-based applications in agriculture
HTML: 1441
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Authors
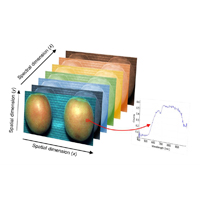
The measurement of vegetation indexes that characterise the plants growth, assessing the fruit ripeness or detecting the presence of defects and diseases, is a key factor to gain high quality of fruit or vegetables. Such evaluation can be carried out using both destructive and non destructive techniques. Among non-destructive techniques, hyperspectral imaging (HSI), combining image analysis and visible/near-infrared spectroscopy, looks particularly useful. Many studies have been published concerning the use of hyperspectral cameras in the agronomic and food field, especially in controlled laboratory conditions. Conversely, few studies described the application of HSI technology directly in field, especially involving ground-based systems. Results suggest that this technique could be particularly useful, even if the role of environmental variables has to be considered (e.g., intensity and incidence of solar radiation, wind or the soil in the background). In this paper, recent in-field HSI applications based on ground systems are reviewed.
How to Cite
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.

 https://doi.org/10.4081/jae.2020.1030
https://doi.org/10.4081/jae.2020.1030



